What is the Management Style of the Bureaucratic Leader?
1. Definition of the Bureaucratic Leader: main characteristics
The Bureaucratic Management style has the following characteristics:Rules and procedures: Bureaucratic Leaders rely on clear and precise rules, procedures, and policies to lead their team and make decisions.
Formal structure: The organizational structure is formal and hierarchical, with a clear chain of command.
Authority: Bureaucratic Leaders have formal authority and rely on their position to exercise their power.
Control: Bureaucratic Leaders closely control the activities and performance of their employees.
Rigidity: Bureaucratic Leaders can be perceived as rigid and inflexible, as they strictly adhere to rules and procedures.
2. Origins of Bureaucratic Leadership
The theory of Bureaucratic Leadership is often associated with the theory of bureaucracy developed by sociologist Max Weber in the early 20th century. Weber described bureaucracy as a mode of organization that relies on clear rules and procedures, a well-defined hierarchy, and specific roles and responsibilities for each member of the organization. According to Weber, bureaucracy is an effective way to organize large organizations, as it allows for the rational and predictable coordination of the activities of many individuals.
Weber identified three types of legitimate authority that can be used to exercise power in an organization: traditional authority, charismatic authority, and rational-legal authority. Rational-legal authority, which is based on established rules and procedures, is the one most associated with Bureaucratic Leadership.
Since Weber's work, many other researchers have studied bureaucracy and Bureaucratic Leadership, and have made significant contributions to the theory. For example, the work of Robert K. Merton highlighted some of the potential dysfunctions of bureaucracy, such as rigidity and resistance to change. Other researchers have examined how Bureaucratic Leadership can be adapted to be more effective in different organizational contexts.
Today, Bureaucratic Leadership is one of many Management styles that are studied in management and Leadership. It is often compared and contrasted with other Management styles, such as transformational Leadership, participative Leadership, and situational Leadership, to help understand the advantages and disadvantages of each approach.
3 Strengths and Critiques of the Bureaucratic Leader Style
3.1 Strengths
Bureaucratic Leadership has several strengths that can be beneficial for certain types of organizations and situations. Here are some of the advantages of this Management style:
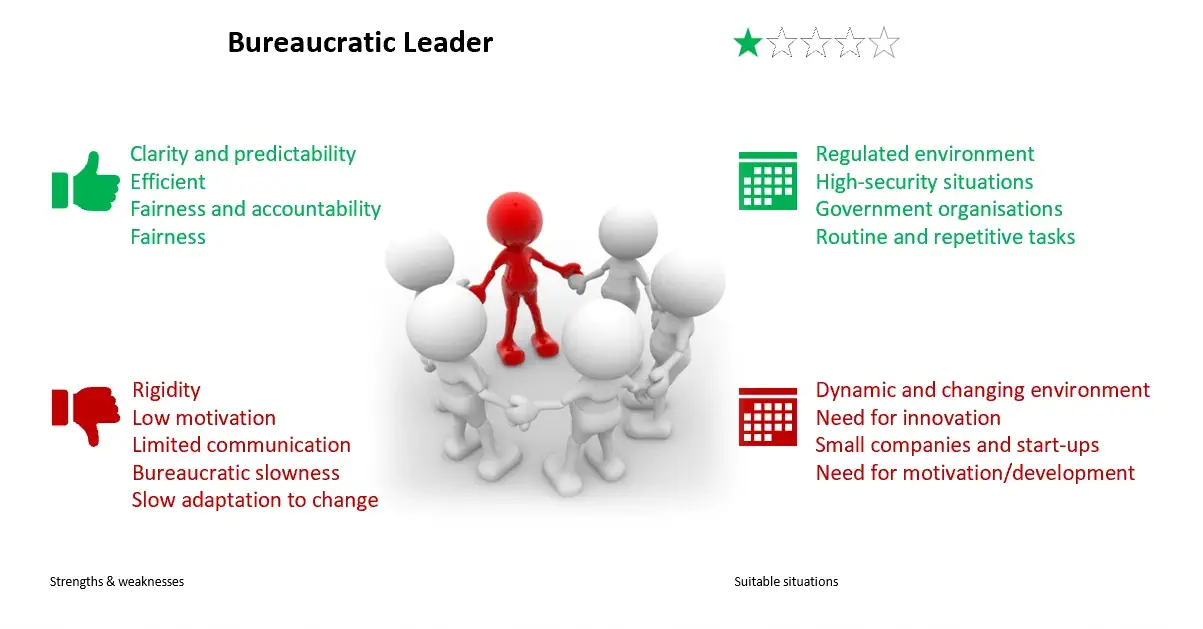
Clarity and predictability: Clear rules, procedures, and policies allow employees to know exactly what is expected of them, which can foster an orderly and predictable work environment.
Efficiency: In situations where it is important to follow precise procedures, such as in regulated industries or organizations dealing with safety issues, Bureaucratic Leadership can be very effective in ensuring that all necessary steps are consistently followed.
Fairness: By relying on established rules and policies, Bureaucratic Leaders can ensure that decisions are made fairly and objectively, rather than based on favoritism or subjectivity.
Stability: Bureaucratic Leadership can bring stability to an organization, as employees know what is expected of them and leaders have clear authority to make decisions and manage resources.
Accountability: The formal and hierarchical structures of Bureaucratic Leadership allow for clear accountability of individuals' actions, which can help maintain high standards of performance.
3.2 Critiques or Faults of the Bureaucratic Style
Here are some of the main weaknesses of Bureaucratic Leadership:
Rigidity: Bureaucratic Leaders can be perceived as rigid and inflexible, as they strictly adhere to rules and procedures. This can hinder innovation and adaptability, which are often required in today's fast-paced business environment.
Resistance to change: Bureaucratic Organizations can be resistant to change, as the emphasis on rules and procedures can make it difficult to implement new ideas or respond to changing circumstances.
Lack of employee autonomy: The reliance on rules and procedures can also restrict employee autonomy and creativity, which can be demotivating and hinder performance.
Inflexibility in dealing with complex situations: Bureaucratic Leadership can be less effective in dealing with complex and ambiguous situations, as the reliance on rules and procedures may not allow for the flexibility needed to respond effectively.
Dependency on the leader: Employees may become overly dependent on the leader to make decisions and provide direction, which can limit their ability to work independently and develop their skills.
4. Situations in Which the Bureaucratic Leader style is suitable
Bureaucratic Leadership is generally well-suited to situations where it is essential to comply with strict rules, procedures, and regulations. Here are some examples of situations where the Bureaucratic Management style can be effective:
Regulated industries: In highly regulated industries, such as finance, health, and aerospace, compliance with rules and regulations is essential to avoid penalties and ensure the safety of products or services.
Safety situations: In situations where safety is a major concern, such as in nuclear facilities, chemical plants, or military operations, Bureaucratic Leadership can help ensure that all safety procedures are followed to the letter.
Governmental organizations: Governmental organizations often have strict rules and procedures that must be followed, and Bureaucratic Leadership can be effective in ensuring compliance.
Large organizations: In large organizations with many employees and a complex organizational structure, Bureaucratic Leadership can help coordinate activities and maintain order.
Routine and repetitive tasks: For tasks that are routine and repetitive, and that require high precision and uniformity, Bureaucratic Leadership can be appropriate.
5. Situations in Which the Bureaucratic Leader style is Not suitable
The Bureaucratic Management style may be less suitable in the following situations:
Dynamic and rapidly changing environments: In industries or environments where changes are frequent and rapid, Bureaucratic Leadership may be too rigid and slow to adapt effectively.
Innovation and creativity: Organizations that rely on innovation and creativity, such as tech companies or startups, may find that Bureaucratic Leadership stifles the flexibility and risk-taking necessary to innovate.
Small businesses and startups: Small businesses and startups, which often need to be agile and flexible, may find that Bureaucratic Leadership is too rigid and formalized for their organizational culture.
Teamwork and collaboration: Environments that value teamwork, collaboration, and open communication may be hindered by the hierarchical structure and formal procedures of Bureaucratic Leadership.
Employee motivation: Employees seeking autonomy, flexibility, and personal development opportunities may feel limited and demoralized by the Bureaucratic Management style.
6. Conclusion: nowadays, the Bureaucratic Leader style is somewhat outdated but may be appropriate in certain highly regulated situations
 Bureaucratic Leadership can be seen as outdated in the current context of the business environment, which is characterized by rapid change, innovation, and flexibility. The modern world of work tends towards flatter organizational structures, open communication, and a more participative or transformational Management style.
Bureaucratic Leadership can be seen as outdated in the current context of the business environment, which is characterized by rapid change, innovation, and flexibility. The modern world of work tends towards flatter organizational structures, open communication, and a more participative or transformational Management style.
That said, there are always situations where Bureaucratic Leadership can be appropriate and effective, especially in highly regulated environments or situations where safety is a major concern. In addition, some elements of Bureaucratic Leadership, such as clarity of roles and responsibilities, can be beneficial in any organizational context.
In the end, whether Bureaucratic Leadership is a "good" or "bad" Management style depends on the specific situation and the needs of the organization. An effective Management style often involves combining different styles and approaches to meet the unique needs of the organization and its employees. It is therefore important for leaders to develop a range of Leadership skills and know when to use each style based on the situation.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.


Comments