Practical implementation of 5S methodology
1. What is the 5S methodology and its benefits
The 5S is a cleaning and storage technique whose five letters mean:- Seiri: Sort, separate the necessary from the unnecessary
- Seiton: Set in order
- Seiso: Shine, clean
- Seiketsu: Standardize
- Shitsuke: Sustain, self-discipline

Benefits of the 5S methodology
The 5S methodology is actually much more than a cleaning technique. When it is used according to its true intentions, the benefits are multiple:
- cost reduction by eliminating unnecessary tools or parts (Seiri) or standardizing them (Seiketsu)
- simplifying work and increasing productivity by reducing search times (Seiton)
- prevention of breakdowns by inspecting tools or machines during cleaning (Seiso) and detecting any anomalies
- reduction of the risk of accidents, for example by avoiding the cluttering of parts, or places made slippery by oil stains
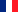
2. Implementation of 5S methodology - A project approach
The implementation of the 5S method requires time and resources. 5S is highly visible in the field. It requires effort, at least initially, and discipline from employees. 5S changes the working habits of many people. What's more, the benefits of 5S are not very visible and not always tangible. There may even be none if it is poorly implemented and is just a cleaning method.All these ingredients make it a genuine change project, which needs to be supported by management over the long term (beyond providing the resources for initial implementation), accepted by employees and actually used to produce the expected benefits.
In the following paragraphs, we will detail a project approach that has proved its worth in many organisations, as illustrated below.

3. The five steps of the implementation of the 5S methodology
3.1 Diagnosis
Identify current problems, areas for improvement and associated issues in the different areas of the defined scope.(Continue to) show the value of implementing the 5S methodology: this objective is generally achieved by showing managers the results related to the first objective. Ii is essential to ensure support from management but also from middle management. Indeed they may still be reluctant to implement an approach that could be perceived as additional "cleaning" tasks without much interest.
3.2 Prepare the project
Define the objective of the project and its target: define the purpose of the 5S methodology and the level of challenge or expected savingsSelect either the application areas and areas of improvement to be implemented: the project may well cover only part of the initial scope (e.g. some workshops and not others, production or maintenance...) or not seek to solve all the problems identified. Choose the pilot.
Define the project elements:
- the implementation planning (duration of pilot, durations per zone or per type of improvement...)
- the implementation team and the roles and responsibilities of each member
- the monitoring mechanism
- the necessary budget.
3.3 Pilot
Train the first people, the project team and the staff of the pilot area.Implement each action of the 5S methodology on the pilot (see details below).
Show savings: make the savings visible in order to show the interest of the process and motivate the team; check that the savings correspond to the initial estimated savings
Improve the method: the pilot is also used to test the implementation of the approach before deploying it in other areas.
3.4 Implementation
Train the rest of the staff as their zones are deployed.Integrate into the operational system: integrate the 5S methodology into operational life, managerial follow-up and support functions; for example in team meetings, dashboards, training, etc.
Measure and communicate savings: an essential step to continue to demonstrate the value of the approach, from operational to top management (who financed the approach)
3.5 Sustainability
Monitor: - At the beginning, monitor the effective integration into operational modes on a regular basis
- Then, manage the 5S methodology like any other operational mode, integrated into the operating modes... i.e. on a continuous basis with 5S performance indicators
Audit: set up an audit process
4. Actual Implementation of the five "S" actions

Each action of the 5S methodology (Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu and Shitsuke) is implemented in two phases:
- In the pilot phase for the pilot area
- in the deployment phase for each other targeted area
The 5S methodology can be used in different environments, in production plants or offices, so we use the word "element" which can be a part, tool, object or other depending on the environment.
The implementation uses the same methodology regardless of the environment.
Actions Implementation figure

4.1 Implementation of actions: Preparation
Before entering into the heart of the "S" implementation, there is a small but important preparation phase, described here.
For each area where implementation applies, for the pilot or deployment:
- (Re)explain to the person in charge of the area concerned the whole process; the site director must participate at least initially in this exchange to indicate the importance of the process
- Train staff
- Ensure that at least one person from the team responsible for the area concerned is involved in the work from start to finish
4.2 Implementation of the 5S actions: Sort
This step of the 5S methodology being the first concrete step, it is very important to devote energy to it. This is where credibility begins to be established.
1. Prepare for temporary storage
- Take pictures of the target area before removing its elements
- Define a place to temporarily store the elements that will be removed
- Prepare colour-coded labels to remove’, "maybe remove ‘, "replace’, "repair'.
Prepare handling equipment if necessary: box, trolley, pallet truck, etc.
2. Perform a first sorting
- Make one for the obvious elements, by moving the targeted elements into the storage area. If the handling equipment is not suitable for sorting "immediately', put the labels remove ‘.
- During this action, put the labels "maybe remove" in case of doubt
- Put labels for the other categories that are obvious (it is optional at this stage, but it is a saving for the next steps)
- List the items put in this area for follow-up
3. Test and monitor
- Install the monitoring board; define and install a visual monitoring board in the target area with three categories:
- “Remove” with two columns :
- one to leave comments if some people think that shouldn’t be removed
- one for those who have taken back or used an element of the area to be removed
- “Remove maybe" with four columns:
- The list of elements with the “remove maybe" labels
- Confirmed
- To be kept
- Comments on the report
- “Remove ideas" with two columns:
- one to write additional ideas for parts to be removed
- one to say why or add comments
- “Remove” with two columns :
- Give a week (or other depending on the organization) for people working on the area to comment, add parts to remove, or remove parts from the "remove" list
- Review the board and the area "to be removed" (if elements have been included) and lead a team meeting
- Review all categories and discuss the adjustment of lists and items to be removed
- Take the opportunity to make a first team tour and ask their opinion on the approach and results of this first step.
- Estimate the savings of the removed items (estimate the frequency and cost of purchase if they remain in the list of items used)
4. Finalise: discard the items to be removed
4.3 Implementation of 5S actions: Set in order
In this step of the 5S methodology, it is essential to focus on time savings. It is not enough to "make it look good", it is necessary to make sure that it will be really practical and that the displacements will be reduced.
1. Define storage areas
- Make a list of the elements to be stored for each sub-area (workshop, office, etc.) of the treated area
- For each element, ask the people who use them how often they are used (prepare columns day, week, month, month, quarter, year, never to facilitate work); note the subpart of the treated area
- Estimate the volume of parts for each periodicity with one detail per sub-area
- For each frequency, identify possible storage locations in the area using the following guidelines:
- The closer the storage place is to the place of use, the more frequently it is used: every day, next to the person; every week, in the surrounding area....
- The size of the site must be well dimensioned with more space than not enough (ease of search)
- Do not put the same type of element in two different places... but limit travel if two remote teams use the same elements
- Review why the two teams are distant; this can mean a redefinition of physical flows and workstations (a reason to deploy the 5S in a broader integrated Lean approach)
- Otherwise, it will be necessary to choose the best solution (to be discussed with the teams) between duplicating the tools or increasing the travel
- Involve teams in the choices
2. Define the location of each element within each area
- Collect the elements by search/use logic and according to specific constraints (safety, humidity...)
- Identify the necessary storage supports, standard (cabinet...) or to be manufactured (template...)
- prefer modular and flexible supports; one thing is for sure, there will be changes!
- If possible, do not purchase anything, or have any manufactured before the next test phase
- Further involve teams in the choices, especially for workstation elements
2. Test and monitor
- Define and implement monitoring means to obtain user feedback and start measuring the change (search and travel time, productivity...)
- It is easy to get feedback for daily use and there will be at least two weekly iterations but higher uses will be more random, so monitoring may need to be done later if the test phase is too long.
- Store each element in its place as defined and operate for at least two weeks.
4. Adjust and install the final supports
4.4 Implementation of 5S actions: Shine
This step of the 5S methodology is often the methodology killer : it is the one that can make people say that 5S is only cleaning. So, it is absolutely necessary to focus on the benefits of cleaning.
1. Do a thorough “reference” cleaning
- Take a picture of each area before cleaning
- Define cleaning and inspection instructions at the same time as cleaning:
- Cleaning instructions: frequencies, cleaning means, people who clean and specific instructions when necessary (disassembly, safety...)
- Inspection: In industrial (factory, warehouse, etc.) or technical (e. g. laboratory) environments, inspection is the greatest added value of cleaning because it helps to prevent breakdowns or work incidents
- Doing it at the same time will allow to test the instructions during the next cleaning.
- Take reference photos
- Photos of the result AND anomalies (if observed) for each area with details for critical elements.
- Add them to cleaning and inspection instructions or other procedures (e. g. self maintenance)
2. Test cleaning and inspection
- Review cleaning and inspection instructions with area managers and adjust if necessary
- Define and implement monitoring means to obtain user feedback
- Carry out the test, if possible at the same time as the "Sort" stage in order to pool monitoring resources and reduce the pilot's total time, unless this delays the test in the "Sort" stage too much
3. Adjust
4.5 Implementation of 5S actions: Standardise
This phase makes it possible to standardise the 5S methodology but also provides an opportunity to detect the lack of standardisation in operating procedures (format, level of detail, content).1. Inventory and Pilot Standardisation
- Make an inventory of the different standards in terms of operating procedures in the different areas; select or define a standard format; this phase must begin before describing the storage and cleaning procedures
- Adjust the standard at the end of the pilot and ensure that all pilot documents or tools are standardised
- Possibly standardise the other procedures, outside the 5S method.
2. Implementation standardisation
- Each deployed area must apply the standards
- Nevertheless, adjustments can be made during deployment based on accumulated experience; continuous improvement begins
4.6 Implementation of 5S actions: Sustain
Unfortunately, this step is often underestimated. People think everything is done. Or project teams are eager to do another project. But the worst is when this phase becomes a top down control.The 5S methodology will only survive if its application brings benefits and its benefits are followed. Then, there is much less need to follow that this or that action is well done. We follow the realization of the actions to understand why the benefits are there or not. We don't follow them just to follow them. So you have to sustain it very early and in three steps:
1. Sustainability starting at the pilot phase
- The sustainability actions are already starting within the pilot since it is at this point that the results measurements begin
- At the end of the pilot, an assessment is made to adjust and complete the measurement system before deployment
2. Sustainability during deployment
- The 5S methodology is integrated into the existing performance monitoring tools and operational ways of working of each deployed area: procedures, visual display, area indicators
- A progress dashboard of actions and results is consolidated as they are deployed
3. Sustainability after deployment
- Results monitoring indicators are integrated into the management dashboards
- An audit process is defined, with a faster frequency at the beginning
5. Conclusion
Although 5S may seem fairly simple, it is difficult to implement on a permanent and widespread basis within an organisation. However, a methodical implementation of 5S, as described here, enables it to be done for the benefit of all: easier day-to-day life for employees, tangible results for managers and financial officers.We therefore hope that this guide will help you to succeed or improve your 5S implementation.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.


Comments 2
How great that you discuss that the 5S method is more than a cleaning method!
Need too enquire on 5's implementation program